Michael Faraday
(22 September 1791 – 25 August 1867) was an English chemist and physicist in the terminology of the time) who contributed to the fields of electromagnetism and electrochemistry.(learn more : www.en.wikipedia.org.)
ภาพ : ชุดการศึกษาของฟาราเดย์
Source : (en.wikipedia.org, 2012)Teaching model : Direct Instrucion Model(DIM)
Keywords :- เครื่องกำเนิดไฟฟ้ากระแสสลับ magnetic flux สมการแรงเคลื่อนไฟฟ้า กระแสไฟฟ้าเหนี่ยวนำ สมการและกราฟ ค่ายังผล(root mean square value) สมบัติเฉพาะตัวของอุปกรณ์ไฟฟ้า(RCL) Phaser diagram วงจรไฟฟ้ากระแสสลับ การต่ออุปกรณ์ไฟฟ้าแบบอนุกรม-แบบขนาน กำลังเฉลี่ย power factor, phase angle Resistance(R), Capacitive reactance(Xc), Inductive reactance(XL) and Impedance(Z)
เนื้อหาสาระ
1. เครื่องกำเนิดไฟฟ้ากระแสสลับ
2. กฎของฟาราเดย์
3. สมการและกราฟ ของกระแสไฟฟ้า-เวลา และความต่างศักย์ไฟฟ้า-เวลา
4. ปริมาณการวัด :ค่าสูงสุด ค่ายังผล(ค่ามิเตอร์หรือ root mean square)
5. สมบัติเฉพาะตัวของตัวต้านทาน(R) ตัวเก็บประจุ(C)และตัวเหนี่ยวนำ(L)
6. Phasor Diagram of R,C & L.
7. การต่ออุปกรณ์ไฟฟ้ากระแสสลับ-แบบอนุกรม
8. การต่ออุปกรณ์ไฟฟ้ากระแสสลับ-แบบขนาน
9. มุมเฟส(phase angle) และแฟกเตอร์กำลัง(power factor)
10. กำลังและพลังงานไฟฟ้า
กิจกรรม : การสืบค้นจากห้องสมุดโรงเรียน
นักเรียนสืบค้น ทำความเข้าใจและสรุปรายงานในเวลา 2 คาบ ดังนี้
1. A.C.Generator
2. สมการและกราฟ จากข้อ 1. คือความสัมพันธ์ v-t , i-t
3. Phasor diagram ของ R,C & L
4. วงจรไฟฟ้ากระแสสลับแบบอนุกรม
5. วงจรไฟฟ้ากระแสสลับแบบขนาน
6. กำลังไฟฟ้าเฉลี่ย แฟกเตอร์กำลัง และมุมเฟส
7. แสดงความคิดเห็นต่อกิจกรรมในวันนี้
A.C.Generator
Source : (ncert.nic.in.2012)
ตัวเก็บประจุ(Capacitor)
ภาพที่ 2 ไฟฟ้ากระแสสลับของตัวเก็บประจุ
source : (www.animations.physics/AC.html.,2011)
Click this for more.. ตัวเก็บประจุไฟฟ้าทบทวนค่าความจุ(จากเรื่องไฟฟ้าสถิต)ตามภาพ
Source :(www.sites.google.com/.., 2012)
Inducion coils.Source : (www.Wikipedia.org,2012)
An induction coil consists of two coils of insulated copper wire wound around a common iron core. One coil, called the primary winding, is made from relatively few (tens or hundreds) turns of coarse wire. The other coil, the secondary winding, typically consists of many (thousands) turns of fine wire. An electric current is passed through the primary, creating a magnetic field. Because of the common core, most of the primary's magnetic field couples with the secondary winding. The primary behaves as an inductor, storing energy in the associated magnetic field. When the primary current is suddenly interrupted, the magnetic field rapidly collapses. This causes a high voltage pulse to be developed across the secondary terminals through electromagnetic induction. Because of the large number of turns in the secondary coil, the secondary voltage pulse is typically many thousands of volts. This voltage is often sufficient to cause an electric spark, to jump across an air gap separating the secondary's output terminals. For this reason, induction coils were called spark coils(www.wikipedia.org,2012)
ความรู้สะสมประกอบการวิเคราะห์วงจร1. สมการรูปแบบ Simple Harmonic Motion
2. กราฟตามสมการข้อ 1.
3. นิยามและสูตรปริมาณที่เกี่ยวข้อง
4. Vector analysis practice.
สรุปหลักสำคัญ
ครูมีความเชื่อว่านักเรียนได้ผ่านกระบวนการเรียนรู้จากคุณครูในห้องเรียนมาแล้ว ขอสรุปด้วยแผนภาพ ดังนี้
Source:(www. aieee.examcrazy.com,2011)
ตัวอย่าง:ข้อสอบคัดเลือกเข้ามหาวิทยาลัยขอนแก่น 2554
ความต้านทานเชิงซ้อน(Impedance: Z)
1. Impedance = resistance + capaciticve reactance + inductive reactance
2. การวิเคราะห์ให้ใช้ vector analysis จากแผนภาพ phasor diagram
Impedance of components
Let's recap what we now know about voltage and curent in linear components. The impedance is the general term for the ratio of voltage to current. Resistance is the special case of impedance when φ = 0, reactance the special case when φ = ฑ 90ฐ. The table below summarises the impedance of the different components. It is easy to remember that the voltage on the capacitor is behind the current, because the charge doesn't build up until after the current has been flowing for a while.
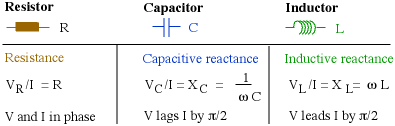
แบบฝึกหัด จงตอบคำถามจากภาพต่อไปนี้
Source:(Uni.Physics.,Holliday&Walkers,1996)
So.. I hope you enjoy your work !
สำหรับศิษย์ 6/4 และ 6/5 หาดใหญ่วิทยาลัย ทุกคนทำการบ้าน 1 และ 2 ส่งครูหลังจากครูบรรยายสรุป
ในห้องเรียนจบเป็นที่เรียบร้อย
* กำหนดการ *
วันศุกร์ที่ 7 กันยายน 2555 กิจกรรม 6/4 และ 6/5 มีดังนี้
1. ทดสอบเก็บคะแนน ทุกบท เวลา 1 คาบ 10 ข้อ แบบเขียนตอบ
2. ส่งการบ้าน 1 และ การบ้าน 2




















